Conjoint: Understanding the Power of Trade-offs in Decision Making
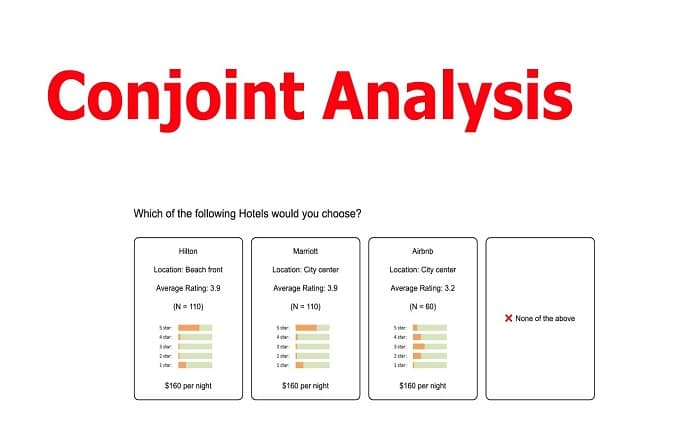
In the world of market research and consumer behavior, understanding the preferences and choices of individuals is crucial for businesses to thrive. One powerful technique that aids in this understanding is conjoint analysis. Conjoint analysis is a valuable tool that allows researchers to dissect the decision-making process by evaluating how people make trade-offs when faced with multiple options. In this article, we will explore the concept of conjoint analysis, its applications, and its significance in gaining insights into consumer behavior.
What is Conjoint Analysis?
Conjoint analysis is a quantitative research technique that helps understand how people make decisions based on the trade-offs they are willing to make. It aims to uncover the relative importance individuals place on different attributes when choosing between various options. By simulating real-life decision-making scenarios, conjoint analysis provides valuable insights into consumer preferences and the factors that drive their choices.
Components of Conjoint Analysis
Conjoint analysis involves three essential components: attributes, levels, and profiles.
Attributes
Attributes are the characteristics or features of a product or service that are considered during the decision-making process. These attributes can be tangible, such as price, size, or color, or intangible, such as brand reputation or customer service.
Levels
Levels represent the different variations or values within each attribute. For example, if the attribute is “price,” the levels could be “$10,” “$20,” and “$30.” The combination of different attribute levels forms the profiles used in conjoint analysis.
Profiles
Profiles are the complete descriptions of a product or service that participants evaluate during the analysis. Each profile consists of specific attribute levels, allowing researchers to measure the impact of different combinations on consumer preferences.
Types of Conjoint Analysis
There are several variations of conjoint analysis, each suited to different research objectives and data collection methods. The three main types are:
Full-profile Conjoint Analysis
Full-profile conjoint analysis presents participants with complete profiles and requires them to rank or rate their preferences. This approach provides detailed insights into the importance of each attribute and level.
Choice-based Conjoint Analysis
Choice-based conjoint analysis presents participants with a series of choice sets, asking them to select their preferred option. By analyzing the choices made, researchers can determine the relative importance of attributes and levels.
Adaptive Conjoint Analysis
Adaptive conjoint analysis is a dynamic approach that adjusts the choice sets based on participants’ previous responses. This method allows for a more efficient and personalized analysis by adapting the options presented to each individual.
Conducting Conjoint Analysis
To conduct conjoint analysis effectively, a systematic approach should be followed. Here are the general steps involved:
Define the Research Objective
Clearly define the research objective and the decisions or insights you aim to gain from the analysis. This will guide the selection of attributes, levels, and data collection methods.
Select Attributes and Levels
Identify the relevant attributes and determine the appropriate levels for each attribute. Consider the factors that are most likely to influence consumers’ decision-making process.
Create Choice Sets or Profiles
Generate a set of profiles or choice sets that represent different combinations of attribute levels. Ensure that the profiles cover the full range of possibilities and are well-balanced.
Collect Data
Administer the conjoint analysis survey to the target audience and collect the responses. This can be done through online surveys, face-to-face interviews, or other suitable data collection methods.
Analyze the Data
Analyze the collected data using appropriate statistical techniques. This analysis will reveal the relative importance of attributes, levels, and their interactions in influencing consumer preferences.
Applications of Conjoint Analysis
Conjoint analysis has diverse applications across various industries. Some of the key applications include:
Product Development and Pricing
Conjoint analysis helps businesses understand which attributes and levels are most appealing to consumers. This insight guides product development, allowing companies to create offerings that align with customer preferences. It also aids in determining optimal pricing strategies based on perceived value.
Market Segmentation
By analyzing preferences across different segments, conjoint analysis enables businesses to identify distinct groups of consumers with similar preferences. This information helps tailor marketing messages and strategies to specific target audiences, maximizing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Advertising and Messaging
Conjoint analysis can be used to assess the impact of different advertising messages and communication strategies. By understanding which attributes and levels resonate with consumers, businesses can optimize their messaging to enhance brand perception and customer engagement.
Benefits of Conjoint Analysis
Conjoint analysis offers several benefits for businesses and researchers:
- Provides a deeper understanding of consumer preferences and decision-making processes.
- Enables accurate measurement of the relative importance of different attributes and levels.
- Facilitates product development and pricing decisions based on customer preferences.
- Helps optimize marketing strategies by tailoring messages to specific target audiences.
- Allows businesses to gain a competitive edge by aligning offerings with consumer demands.
Limitations of Conjoint Analysis
While conjoint analysis is a powerful research tool, it does have certain limitations:
- Assumes rational decision-making, which may not always reflect real-world behavior.
- Requires careful selection of attributes and levels to capture the full range of consumer preferences.
- Can be time-consuming and expensive, especially when using full-profile conjoint analysis.
- Relies on participants’ ability to accurately evaluate and rank preferences, which can be influenced by various factors.
Conclusion
Conjoint analysis is a valuable technique that helps businesses unravel the complexities of consumer decision-making. By understanding how individuals make trade-offs between different attributes, companies can develop products, set prices, and craft marketing strategies that resonate with their target audience. Incorporating conjoint analysis into market research efforts empowers businesses to make informed decisions, gain a competitive advantage, and ultimately drive customer satisfaction and loyalty.



